This document explains how to get an API Key from Google and provides a brief overview about it.
To use Google Maps in any compiled Android application, you must have an API Key from Google. Otherwise, maps will not be shown when using the Maps Control Type or Geolocation domain.
Note: This is not required when prototyping the application through
GeneXus Project Navigator, as it already has its own Maps API Key.
By default, the generated app uses a default Android debug-certificate to sign the application when compiling.
That allows you to install the application on devices, directly with the *.apk file, but not through Google Play (since GeneXus 15 Upgrade 2), unless a custom certificate is created.
However, to use Google Maps service you need a special certificate called Map API Key, different from the previous one. This particular key is linked to the specific package name and the certificate mentioned before, in order to restrict the access.
This section explains how to obtain that key for your application.
The first thing to know is the fingerprint of the certificate that will sign the application (this is not required if while you are prototyping with the debug certificate provided by GeneXus).
To see this fingerprint run the following command, using the keystore provided by Android.
keytool -list -v -keystore <your_release_key.keystore> -alias <your_alias_name> -storepass <your_store_pass> -keypass <your_key_pass>
Where:
| |
Value |
Description |
Default (Android Application Signing) |
| |
<your_release_key.keystore> |
The filepath to the *.keystore file, whose value is set on Key Store File property. |
C:\Users\<user>\.android\debug.keystore |
| |
<your_alias_name> |
The alias of the *.keystore file, whose value is set on Key Alias property. |
androiddebugkey |
| |
<your_store_pass> |
The key store password to access the *.keystore file, whose value is set on Store Password property. |
android |
| |
<your_key_pass> |
The key password to access a particular key pair's private key. |
android |
This command tool will print an output like this:
Alias name: androiddebugkey
Creation date: Dec 01, 2016
Entry type: PrivateKeyEntry
Certificate chain length: 1
Certificate[1]:
Owner: CN=Android Debug, O=Android, C=US
Issuer: CN=Android Debug, O=Android, C=US
Serial number: ********
Valid from: Mon Jan 01 08:04:04 UTC 2013 until: Mon Jan 01 18:04:04 PST 2033
Certificate fingerprints:
MD5: AE:9F:95:D0:A6:86:89:BC:A8:70:BA:34:FF:6A:AC:F9
SHA1: 5F:BD:E1:6B:93:D6:5A:01:D2:C2:43:04:DD:2D:3D:93:A9:AD:C8:E8
Signature algorithm name: SHA1withRSA
Version: 3
The SHA1 value corresponds to the fingerprints.
Note: The keytool program is installed in the /bin directory of Java JDK
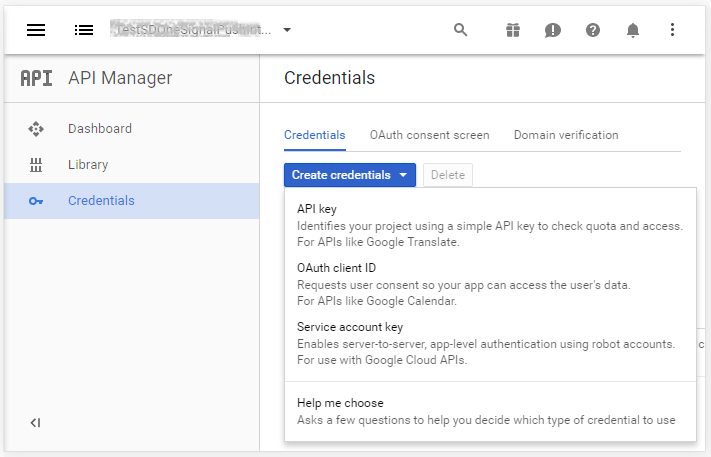
Go to Google API console and create a new API Key for your application.
The process to obtain that key can be done accessing to:
API Manager > Credentials > Create Credential > API Key.
The fingerprint from Step 1 allows adding exclusive access for this application. The following steps explain how to do it.
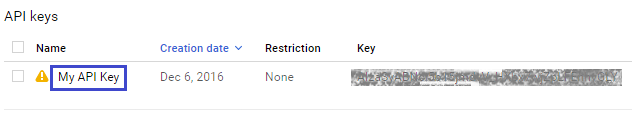
3.1 Select the API key
Click on the API Key created in Step 2 from the list.
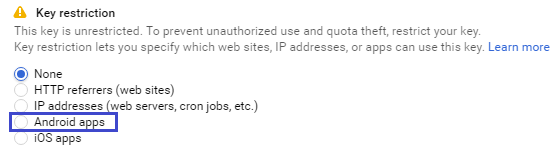
3.2 Check Android apps
On the Key restriction section, check for Android apps option.
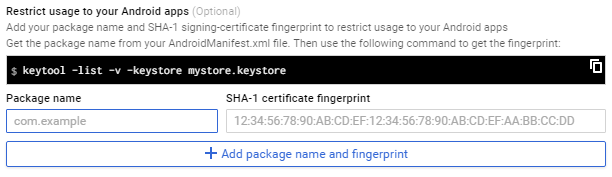
3.3 Add package/fingerprint
Click on "Add new package name and fingerprint" button, and complete the fields with your package name and fingerprint (from Step 1)
3.4. Save your changes
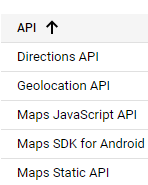
Depending on the case, it is necessary to enable some API, such as: Geolocation API and/or Directions API and/or Maps Static API, etc into the Google Apikey.
Finally, set the Android Maps API Key property with the value of Google API console (notice that there is not longer a warning icon).
Note:
If you have applications in production with the previous default settings (i.e. the *.apk file signed with Artech credentials), you must generate the fingerprint with the legacy values.
Google Maps - First steps
Google Maps - Get API Key