External Objects (EO) with their Type property set to 'Native Object' store all the information (name, properties, methods, and parameters) about how to access a defined Java class, .NET assembly, or JavaScript source.
They are usually called Native Objects and each one of them corresponds exactly to a class of the external resource.
Once you create an External Object and set its Type property to 'Native Object' with the properties and methods exposed by the external resource properly mapped, you can manage these methods and properties inside the GeneXus code.

When generating with .NET and Java generators, the following wizards are available to help you to define the External Object structure:
You can access these wizards by selecting Tools > Application Integration in GeneXus' main menu.
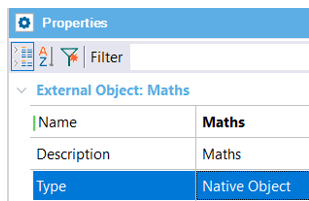
Below are the properties available for the Native Object:
- Name: External Object name.
- Description: External Object description.
- Type: External Object type (set to 'Native Object').
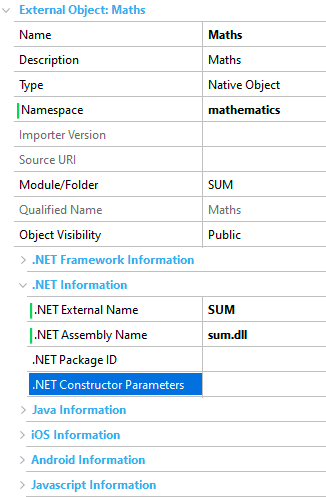
- Namespace: Class namespace.
- Module/Folder: Folder where the External Object is located.
- Object Visibility: Accessibility from other objects located in different Modules.
- .NET/.NET Framework Information
- .NET/.NET Framework External Name: Name of the external class (.dll).
- .NET/.NET Framework Assembly Name: Name of the assembly associated with the External Object.
- .NET/.NET Framework Constructor Parameters: Comma-separated list of parameters to be passed to the assembly constructor. The constructor parameters are always constants.
- .NET Package ID: Uniquely identifies the External Object.
- Java Information
- Java External Name: Name of the external class (.class).
- External Package Name: Name of the package where the class associated with the External Object is located.
- Java Constructor Parameters: Comma-separated list of parameters to be passed to the external class constructor. The class constructor parameters are always constants.
Below are the properties available for each type defined inside the Native Object.

Below are the properties available for each property defined inside the Native Object.

- Property Type: Indicates whether it is a read-only, read/write, or member type property.
- Internal Name: Internal name to be given to the property.
- Description: Description.
- Type: Property data type.
- IsStatic: Indicates if it is static or not (True, False).
- Control Type: Type of control to be shown.
- .NET/.NET Framework Information
- .NET/.NET Framework External Name: External name of the property in the .Net class.
- .NET/.NET Framework External Type: External data type of the property.
- Java Information
- Java External Name: External name of the property in the Java class.
- Java External Type: External data type of the property.
Below are the properties available for each method defined inside the Native Object.

- Internal Name: Internal name of the method.
- Description: Description of the method.
- Type: Data type of the returned value, if any.
- Based on: Determines if it is based on any other data type.
- XML Name: Exposed Name of the method.
- Is static: Determines if it is static or not (True, False).
- External Member Type: The three possible values are Default, Static, and Instance.
- .NET/.NET Framework Information
- .NET/.NET Framework External Name: External name of the method in the .NET class.
- .NET/.NET Framework External Type: External data type of the returned value.
- Java Information
- Java External Name: External name of the method in the Java class.
- Java External Type: External data type of the returned value.
- Java Method Throws Exceptions: Indicates whether the method in the external class sends an exception; the default value is No.
Below are the properties available for each parameter defined inside the Native Object.

- Access Type: Indicates whether the parameter is an input-only, output-only, or input/output parameter.
- Internal Name: Internal name of the parameter.
- Description: Parameter description.
- Type: Parameter data type in GeneXus.
- External Type: External data type of the parameter.
The events should always be defined as static in GeneXus.
Suppose that you have the Native Object shown above (called "Maths").
Next, in a Web Panel object you define a variable called &Maths based on the "Maths" External Object.
In addition, you define an event as follows:
Event enter
&res = &Maths.Sum(&parm1,&parm2) //&parm1 and &parm2 are variables defined in the Web Panel and their values are entered by the end user
EndEvent
The Sum method returns the sum of &parm1 and &parm2 values.
- .NET: In the case of using External Objects to access assemblies, the assembly or assemblies should be copied to the bin directory of the work environment. When the application is deployed, the assemblies must be taken to production.
- Java: In the case of Java classes, take the jar/zip containing the external classes that have to be included in the classpath.
- JavaScript: The JavaScript resources have to be located within the rest of the static resources of the web application. It needs to be referenced in the GeneXus code.
- Vector and matrix values are not supported; only scalar variables are supported.
- Array data types such as String[], Date[] and so on are not supported.
- Enum data types are not supported.
- If there is an EO method called Initialized, or another reserved word, it must be defined with another name but keeping the External Name property.
Types node is available as Beta since GeneXus 18 Upgrade 10.
External Objects for Android
External Objects for iOS Devices
External Objects for Javascript