This article describes all the necessary steps to define an API object (called APICustomers) and declare inside it a ListCustomers service that returns all the Customer data.
Consider a Knowledge Base containing:
1) A Customer Transaction object:
Customer
{
CustomerId*
CustomerName
CustomerLastName
}
Note: The Customer Transaction has Automatic data population.
2) An SDT that is a collection with the same structure as the Customer Transaction:
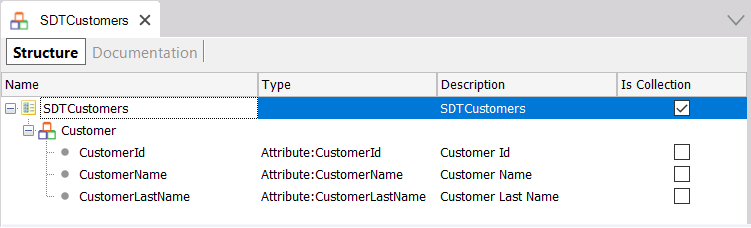
3) A Data Provider object with the logic needed to return all the customer's data:
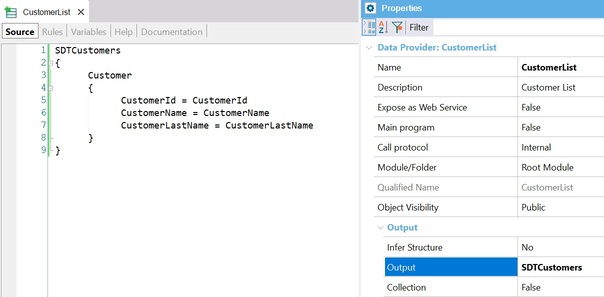
Note that the Data Provider has the previously defined SDT as the output parameter.
Create an API object (by selecting in the main GeneXus Menu File > New > Object) and name it "APICustomers". Inside its Service Source tab, you have to declare, for each service, a mapping between its external name (exposed as a service) and the internal implementation in the KB (in this example, the CustomerList Data Provider). Look at the following mapping:
Customer{
ListCustomers(out:&SDTCustomers) => CustomerList(&SDTCustomers);
}
The external service name is ListCustomers; internally, it is solved with the CustomerList Data Provider.
The service source is not allowed to access data. Therefore, you have to use a Data Provider or a Procedure object instead of a For each command or Business Component.
You could define the following events in the Events tabs, if necessary:
Event Before
//Some Code if is needed
Endevent
Event After
//Some Code if is needed
Endevent
Event ListCustomers.Before
//Some code if is needed
Endevent
Event ListCustomers.After
//Some Code if is needed
EndEvent
The events execution order would be as follows:
- Event 'Before'
- Event 'ListCustomers.Before'
- ListCustomers method (CustomerList Data Provider)
- Event 'ListCustomers.After'
- Event 'After'
You can see all the steps being executed:
Note: This service supports the use of optional HTTP headers to provide additional parameters or metadata during the request. It is useful to pass context-specific information, such as user preferences, local settings, or feature toggles. Read more at
Handling parameters via headers in API Objects methods.
Json Collection Serialization property