To implement gRPC services through the API object, you must set its gRPC Protocol property to True.
After executing a Build, GeneXus automatically generates the following:
- The .proto files in the folder <ModelKB>\web\proto.
- The base code for the protoc compiler.
- The code that implements the services' interface and logic.
Therefore, you only need to determine where the service will be started. To do so, there are two options:
- Web interface.
- Command line.
You may select this option for both the Java generator and the .NET generator.
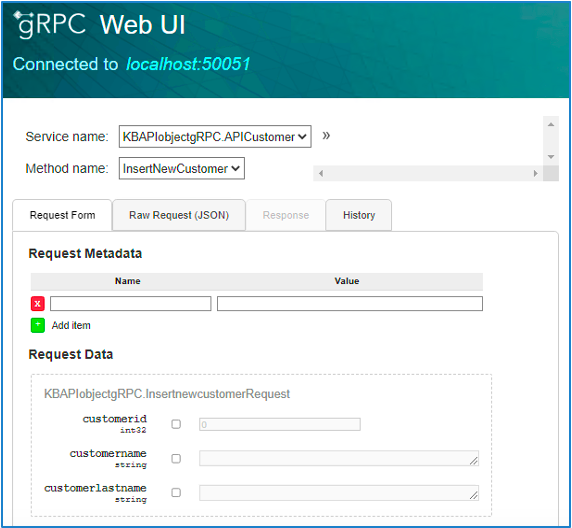
You just need to set the gRPC Protocol property to True, and the Generate OpenAPI interface property to No.
Then execute the API object by right-clicking on it. This will generate, in your browser, an interactive web interface for gRPC like the one below:
You can use a command line tool that provides interaction with the gRPC services, such as gRPCurl.
First, set the gRPC Protocol property to True for the API object, and execute a Build in GeneXus to generate the required files.
The procedure will vary depending on the generator used (Java or .NET).
From the toolbar, go to Tools>CMD Environment Directory.
Then add the line shown below and press enter:
cd Web\build\classes\java\main
This folder contains the compiled code.
You should then execute the following line to start the server:
java -cp ./;../../../libs/* com.<gRPC Package>.<API object name>grpcserver
The libs folder contains all the Java libraries and JAR files necessary to execute any proc command line. Also, you must indicate the value given to the gRPC Package property, as well as the name of your API object with the suffix grpcserver.
For example, if the value of the gRPC Package is KBAPIobjectgRPC and the name of the API object is APICustomer, then you will have to enter the following:
java -cp ./;../../../libs/* com.kbapiobjectgrpc.apicustomergrpcserver
If everything is working correctly, you will get a message like this:
com.kbapiobjectgrpc.apicustomergrpcserver start
INFO: Server started, listening on 50051
This is an indication that the service is ready to be run.
If you wish, for example, to run the service with the gRPCurl tool you must go to the toolbar, Tools>CMD Environment Directory, and run the following:
cd Web
This is where the proto folder is located, containing the .proto files.
Then execute the following line:
<path grpCurl> -plaintext -import-path ./proto -proto <API object name>.proto -d "{\"var\": value, \"var\": \"steingvalue\"}" localhost:<port> <gRPC Package>.<Services base path>
First, specify the path to the gRPCurl executable. Next, provide the filename and path of the .proto file. You will have to indicate the parameters according to you API’s definition. Finally, indicate the port and the values of the gRPC Package property and Services base path property.
When you have defined an API object as follows:
Customer
{
InsertNewCustomer(in:&CustomerId, in:&CustomerName, in:&CustomerLastName, out:&Customer)
=> InsertNewCustomer(in:&CustomerId, in:&CustomerName, in:&CustomerLastName, out:&Customer);
}
And if the value of the gRPC Package is KBAPIobjectgRPC, and the value of the Services base path property is APICustomer, your command should be as shown below:
C:\grpCurl\grpcurl -plaintext -import-path ./proto -proto apicustomer.proto -d "{\"customerid\": 1, \"customername\": \"Simon\", \"customerlastname\" : \"Taylor\" } " localhost:50051 KBAPIobjectgRPC.APICustomer/InsertNewCustomer
If everything is correct, you will get this:
{
"customer": {
"customerid": 1,
"customername": "Simon",
"customerlastname": "Taylor"
}
}
Starting the service in .NET is much easier, because an .exe file is generated in the /web/bin folder.
From the toolbar, go to Tools > Explore Target Environment Directory to open the file explorer in the web folder. Then go to the bin folder to find the file corresponding to the API object name, with the _grpc.exe suffix and double-click on it. For instance, if the name of the API object is APICustomer, the file will be apicustomer_grpc.exe.
When the server has started correctly, you will get something like this:
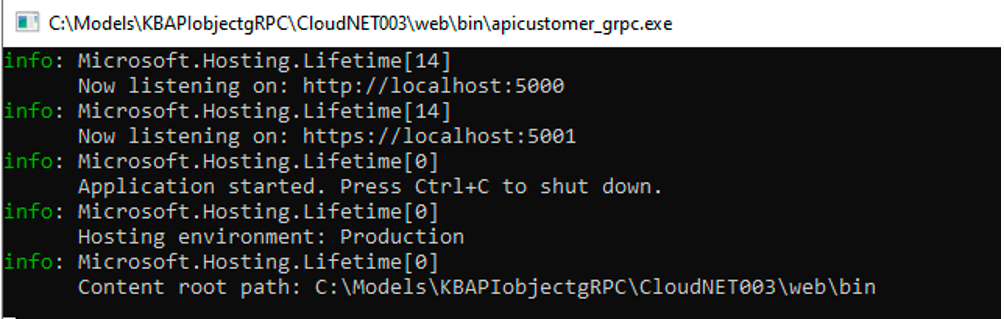
This is an indication that the service is ready to be run.
Therefore, as in the case of Java, you may run the service with the gRPCurl tool.
Return to the toolbar, Tools>CMD Environment Directory, and run the following:
cd Web
That is the location of the proto folder, which contains the .proto files.
Then execute the following line:
<path grpCurl> -insecure -import-path ./proto -proto <API object name>.proto -d "{\"var\": value, \"var\": \"steingvalue\"}" localhost:<port> <gRPC Package>.<Services base path>
Note that it is similar to Java. The only difference is that you must add insecure to indicate that there is no security schema defined.
GeneXus makes it possible to model API services accessible to both gRPC and REST protocols. This means that the implementation of API REST and API gRPC are independent, so you may implement one of them or both at the same time, and the consumer of the services decides according to their needs.
API object Syntax
Test gRPC services with Postman or gRPCurl in ASP.NET Core