You can formally represent geographical entities with the Geography data type. This implies that at the database level, geographical information is stored using specific data types supported by different database management systems.
There are specialized variants of the Geography data type, named GeoPoint, GeoLine, and GeoPolygon types. They are derived from the Geography data type.
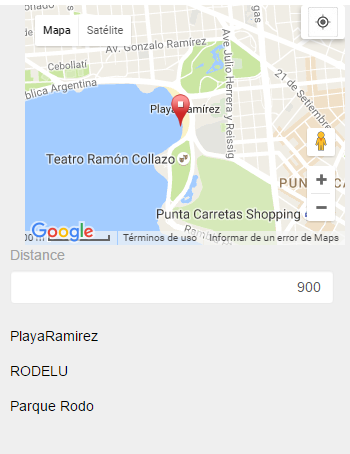
Closest Points
|
Suppose you need to store tourist attractions, so you define the following Transaction object:
Place
{
PlaceId*
PlaceName --> Character data type
PlaceGeo --> Geography data type
}
After that, you define a Web Panel object in which, given any point and a distance in meters, it displays all tourist attractions located within that radius from the point.
&MyPoint --> Geography data type
&Distance --> Numeric data type
Event Load
For each Place
where PlaceGeo.Distance(&MyPoint) < &Distance
&PlaceName=PlaceName
load
endfor
EndEvent
|
 |
Point in a Polygon
|
Consider the following Transaction object:
Neighborhood
{
NeighborhoodId*
NeighborhoodName --> Character data type
NeighborhoodPlace --> Geography data type
}
Suppose you define a Web Panel object in which, given a specific tourist attraction (the end user indicates the point in the map), it shows the neighborhood or zone where that attraction is located:
&MyPoint --> Geography data type
&NeighborhoodPlace --> Geography data type
Event 'Get_Neighborhood'
For each Neighborhood
Where NeighborhoodPlace.Intersect(&Mypoint)
&NeighborhoodId = NeighborhoodId
&NeighborhoodName = NeighborhoodName
&NeighborhoodPlace = NeighborhoodPlace
endfor
Endevent
|
 |
Consider the following Transaction object:
Place
{
PlaceId*
PlaceName --> Character data type
PlaceGeo --> Geography data type
}
You can run the Transaction and double-click on the map associated with the PlaceGeo attribute present in the Layout. When saving, the Geography data will be stored for the place record.
In addition, you can use the FromWkt and FromGeoJSON methods to load data into an attribute based on the Geography data type.
Although the FromString method could be used, the one to be used is the FromWkt method.
Consider the following Transaction object:
Place
{
PlaceId*
PlaceName --> Character data type
PlaceGeo --> Geography data type
}
The PlaceGeo attribute is defined based on the Geography data type to store Points, Lines, or Polygons as needed.
The first three samples below store Points. If the PlaceGeo attribute were of the GeoPoint data type, the same proposed syntax would apply identically.
The other examples store Line and Polygon data in the PlaceGeo attribute. The same proposed syntax would apply identically if the PlaceGeo attribute were of the GeoLine or GeoPolygon data type, respectively.
New
PlaceId = 1
PlaceName = "Palacio Legislativo"
PlaceGeo = GeoPoint.New(-34.8910275746741, -56.18720064473088)
endNew
New
PlaceId = 2
PlaceName = "Golf Club"
PlaceGeo.FromWkt("POINT(-56.163740158081055 -34.92478600243492)")
endNew
New
PlaceId = 3
PlaceName = "Ramirez Beach"
PlaceGeo.FromGeoJson('{"type":"Point","coordinates":[-56.1701774597168,-34.91676309400329]}')
endnew
New PlaceId = 4
PlaceName = "Constituyente, Avenue"
PlaceGeo.FromGeoJson('{ "type": "LineString", "coordinates": [ [ -56.18528366088867, -34.90571271703311 ], [ -56.17850303649902, -34.90641660705113 ], [ -56.15318298339844, -34.9140182347531 ], [ -56.14863395690918, -34.91521472314688 ] ] }')
endnew
new
PlaceId = 5
PlaceName = "Punta Carretas, Neighborhood"
&geojsonNeighborhood = '{ "type": "Polygon", "coordinates": [ [ [-56.148808,-34.918453], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.154835,-34.917061' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.156059,-34.916466' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.156250,-34.914318' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.162754,-34.914791' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.162003,-34.921761' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.165714,-34.919930' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.165737,-34.919930' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.168247,-34.919525' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.169598,-34.918205' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.171421,-34.919209' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.172668,-34.919685' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.172558,-34.920406' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.171207,-34.921566' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.171852,-34.924698' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.171249,-34.925278' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.169662,-34.925438' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.165329,-34.927372' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.161766,-34.929379' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.159920,-34.930645' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.157967,-34.927776' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.156445,-34.927177' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.153141,-34.925507' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.151508,-34.924644' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.151489,-34.923008' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.149151,-34.921497' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.148506,-34.921585' + '], ['
&geojsonNeighborhood = &geojsonNeighborhood + '-56.148808,-34.918453' + '] ] ] }'
PlaceGeo.FromGeoJson(&geojsonNeighborhood)
endnew
New
PlaceId = 6
PlaceName = "Bulevar Artigas, Boulevard"
PlaceGeo.FromString("LINESTRING(-56.16090774536133 -34.928797162523516, -56.1650276184082 -34.89494244739731)")
endnew
new
PlaceId = 7
PlaceName = "Cerro, Neighborhood"
PlaceGeo.FromString('POLYGON ((-56.248367 -34.873821, -56.266563 -34.876427, -56.263733 -34.890366, -56.268799 -34.893394, -56.26897 -34.900291, -56.264851 -34.902615, -56.253605 -34.895645, -56.247597 -34.895153, -56.246052 -34.889523, -56.248367 -34.873821, -56.248367 -34.873821))')
endnew
Geography data type Sample
To view a geographical variable or attribute in the form, only one provider is used: GoogleMaps. For this, you must configure an API Key.
In the case of Android apps, you must configure the Android Maps API Key property.
In the case of Web Panels, you must configure the API Key for each control in the form, as follows:
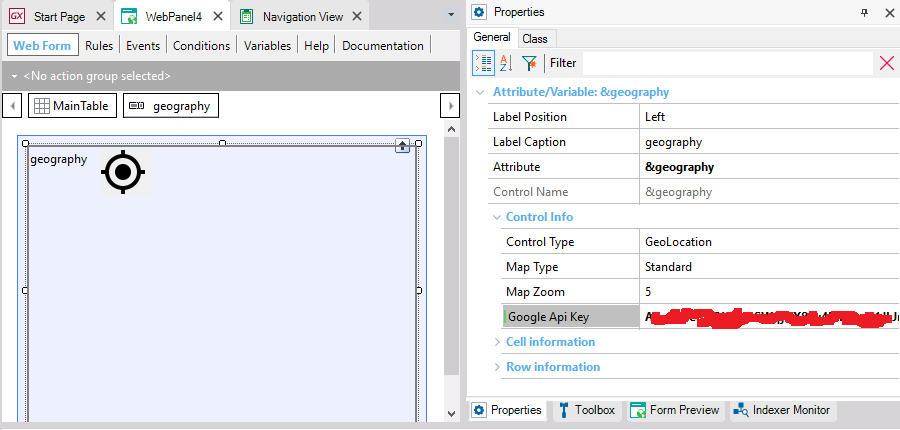
To obtain an API Key for JavaScript, click here.
For it to work properly, most likely you will need to enable more than one API for this Key. For Example: Maps JavaScript API, Maps static API, Geocoding API, Geolocation API are commonly used.
SQL Server: Version 2008 or higher is required.
In the case of SQL Server 2014 or higher, the SQL Server 2012 Feature pack must be installed on the web server.
MySQL/MariaDB: Version 5.7.5 or higher.
Version 8.0 is not supported yet.
Oracle: Oracle Locator or Oracle Spatial installed. For Oracle 11.g or higher, it’s already installed by default.
PostgreSQL: It’s necessary to install the PostGIS extension from PostgreSQL. At the time of database creation, you must set the value “postgis” in the property “PostgreSQL Extensions” (before executing the reorganization).
DBMS: In GeneXus 15, in DB2 and Informix this functionality is not supported.
In previous versions, to represent geographical information some functionalities were used, such as:
- Geolocation domain (Deprecated)
- Map User Control in Web Panels (Available)
- Grid with Control Type = Maps in Panels (Available)
- Geolocation external object (Available)
| Property |
Type Returned |
Description |
| Srid |
int |
Spatial Reference System Identifier (SRID). Identifies the reference system for the represented Geographic object.
See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SRID |
| FeatureType |
Character |
String with the type name of the represented Geographic object.
Some supported types are POINT, LINE, and POLYGON; other supported types can be added in future releases.
The empty string represents the null or unsupported object. |
| Method |
Type Returned |
Description |
| FromWKT(Character) |
Geography |
Loads data into an attribute or variable based on the Geography data type from a representation in WKT format. |
| FromString(Character) |
Geography |
Analogous to the FromWkt method. Use the FromWkt method. |
| FromGeoJSON(Character) |
Geography |
Loads data into an attribute or variable based on the Geography data type from a representation in GeoJSON format.
|
| ToGeoJSON() |
Char |
Returns the GeoJSON representation of a Geography, GeoPoint, GeoLine, or GeoPolygon data type. |
| ToWkt() |
Char |
Converts the Geography data to WKT format. |
| Distance(Geography) |
Int |
Calculates the distance (in meters) between the Geography to which the method is applied and the parameter (both Geography data type must be GeoPoints or Geography containing a GeoPoint). |
| Intersect(Geography) |
Boolean |
Returns true if the Geography parameter intersects or is included in the Geography to which the method is applied. |
| ToGeoPoint(Geography) |
GeoPoint |
Converts the Geography to a GeoPoint type. |
| ToGeoLine(Geography) |
GeoLine |
Converts the Geography to a GeoLine type. |
| ToGeoPolygon(Geography) |
GeoPolygon |
Converts the Geography to a GeoPolygon type. |
There is also a static version of these methods.
Note: FromString and ToString methods are enabled for Geography data types just for compatibility reasons. Use FromWkt and ToWkt methods instead.
DBMSs: SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL, SAP Hana, PostgreSQL
Generators: .NET, .NET Framework, Java, Android, Apple